Difference between common brake medical casters and central locking casters
Here's a detailed explanation of the differences between common brake medical casters and central locking casters:




Common Brake Medical Casters:
1.Functionality: Common brake medical casters are designed with individual brakes on each wheel. These brakes can be engaged or disengaged independently, allowing for individual wheel locking.
2.Operation: Each wheel of a common brake caster has its brake mechanism that needs to be engaged or disengaged separately. This is typically done manually by pressing on the brake pedal or lever associated with each wheel.
3.Flexibility: The individual brakes on common brake casters provide flexibility in maneuvering medical equipment. Each wheel can be locked or unlocked independently, allowing for precise control over the movement of the equipment.
4.Locking Mechanism: Common brake casters usually employ a mechanical braking system that involves friction between the wheel and the brake pad. When the brake is engaged, the brake pad presses against the wheel, preventing it from rotating.
5.Application: Common brake medical casters are commonly used in medical equipment such as hospital beds, stretchers, medical carts, and other devices where precise mobility control is required.
6.Advantages:
Individual wheel control allows for more precise maneuvering of medical equipment.Can be useful when only certain wheels need to be locked while others remain mobile.Provides flexibility in navigating tight spaces and corners.
7.Disadvantages:
* Engaging and disengaging individual brakes can be time-consuming, especially if multiple wheels need to be locked or unlocked.
* Requires more effort and attention from the user to operate each brake individually.
* May lead to uneven locking if brakes are not engaged uniformly.
Central Locking Casters:

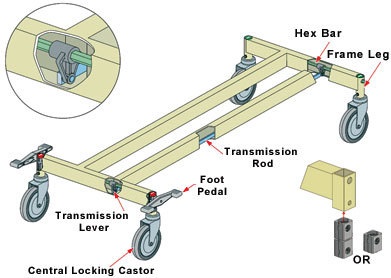
1.Functionality: Central locking casters have a single pedal or lever that, when engaged, locks or unlocks all wheels simultaneously.
2.Operation: The central locking system allows for quick and easy activation or deactivation of all wheel brakes at once. This is typically done by pressing a pedal or lever located in a central position.
3.Locking Mechanism: Central locking casters employ a mechanism that connects all the wheels together, so when the central lock is engaged, it simultaneously activates the brakes on all wheels, preventing them from rotating.
4.Safety: Central locking casters offer enhanced safety by ensuring that all wheels are securely locked with a single action. This reduces the risk of accidental movement, providing stability and preventing potential accidents.
5.Convenience: The central locking system simplifies the process of locking or unlocking the wheels. With a single action, users can immobilize or release all the wheels simultaneously, saving time and effort.
6.Application: Central locking casters are commonly used in various applications where rapid immobilization of equipment is necessary. This includes airline trolleys, industrial carts, medical devices, and other situations where frequent locking and unlocking of wheels are required.
7.Advantages:
* Simultaneous activation of all brakes provides quick and efficient immobilization of equipment.
* Offers convenience and ease of use, particularly in scenarios where multiple casters need to be locked or unlocked simultaneously.
* Ensures uniform locking of all wheels, minimizing the risk of uneven movement.
Disadvantages:
* Limited flexibility compared to individual brake casters, as all wheels are locked or unlocked together.
* May not be suitable for applications where selective wheel locking is required.
* Central locking systems may require additional mechanisms and components, making them more complex and potentially more expensive.
In conclusion, the main difference between common brake medical casters and central locking casters lies in their locking mechanisms and operation. While common brake casters offer individual wheel control and flexibility, central locking casters provide quick and simultaneous immobilization of all wheels, enhancing safety and convenience in various applications. The choice between the two depends on specific requirements.

 English
English Spanish
Spanish German
German Russian
Russian Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese Italian
Italian French
French Hebrew
Hebrew Turkish
Turkish